Biomass

BIOMASS
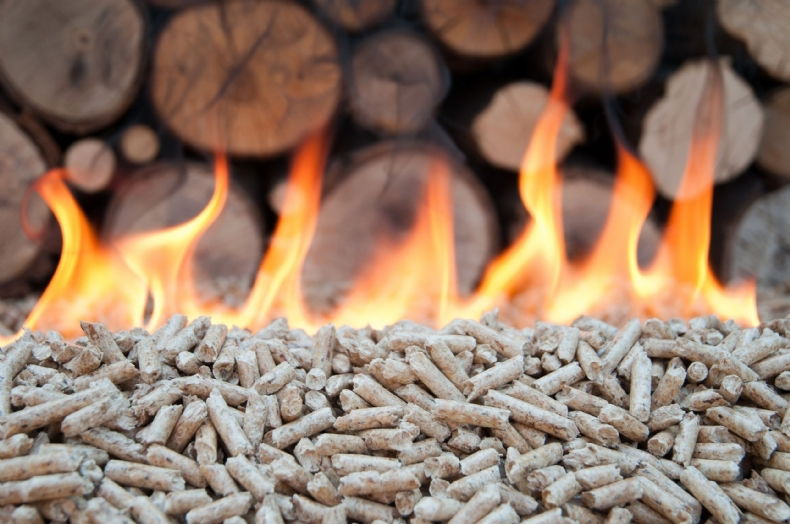
Biomass is plant or animal material used for energy production (electricity or heat), or in various industrial processes as raw substance for a range of products. It can be purposely grown energy crops (e.g. miscanthus, switchgrass), wood or forest residues, waste from food crops (wheat straw, bagasse), horticulture (yard waste), food processing (corn cobs), animal farming (manure, rich in nitrogen and phosphorus), or human waste from sewage plants.
Burning plant-derived biomass releases CO2, but it has still been classified as a renewable energy source in the EU and UN legal frameworks because photosynthesis cycles the CO2 back into new crops. In some cases, this recycling of CO2 from plants to atmosphere and back into plants can even be CO2 negative, as a relatively large portion of the CO2 is moved to the soil during each cycle.
Cofiring with biomass has increased in coal power plants, because it makes it possible to release less CO2 without the cost associated with building new infrastructure. Co-firing is not without issues however, often an upgrade of the biomass is most beneficial. Upgrading to higher grade fuels can be achieved by different methods, broadly classified as thermal, chemical, or biochemical.

BIOGAS
Biogas is the mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen (anaerobically), primarily consisting of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas can be produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste or food waste. Biogas is a renewable energy source. In India, it is also known as "Gobar Gas".
Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion with methanogen or anaerobic organisms, which digest material inside a closed system, or fermentation of biodegradable materials. This closed system is called an anaerobic digester, biodigester or a bioreactor.
Biogas is primarily methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), moisture and siloxanes. The gases methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide (CO) can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel; it can be used for any heating purpose, such as cooking. It can also be used in a gas engine to convert the energy in the gas into electricity and heat.
BIOGAS PLANT
Principle of the Biogas production:
Biogas is produced through the "anaerobic fermentation" process in the "presence of water".
Working of the Biogas production:
1. The biomass is mixed with "cow dung" and "water" in the tank to form a slurry.
2. The slurry is injected into the digester chamber.
3. The digester chamber is kept for fermentation for nearly two months without any disturbance.
4. Only by the end of the two months, the biogas is formed.
We can use the biogas for cooking or some other purposes. We can also remove the formed biogas in the regular interval of period.
ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Biomass is always and widely available as a renewable source of energy. | Biomass energy is not as efficient as fossil fuels |
It is carbon neutral fuel. | It is not entirely clean |
It reduces the overreliance on fossil fuels. | Can lead to deforestation. |
Is less expensive than fossil fuels. | Biomass plants require a lot of space. |
Biomass production adds a revenue source for manufacturers. | |
Less garbage in landfills. |
based on a school project
follow us on:
twitter- @HowLifeGoesOn1
instagram- @howlifegoeson_blog



